Management of Persistent, Recurrent Dermatitis
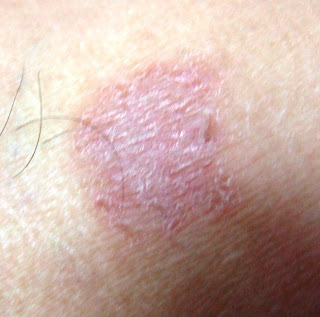
Management of Persistent, Recurrent DermatitisChronic eczema treatment involves topical steroids, immunomodulators, intralesional steroids and other supportive therapy to get rid of the persistent or recurrent dermatitis.
Most dermatitis can go into a chronic stage whereby there are remissions and exacerbations depending upon the triggers and the constitution of the patient. Common chronic eczemas include lichen simplex chronicus (neurodermatitis), chronic stage of atopic eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, dry eczema etc.
More on Chronic Eczema Treatment